Differentiating SDET and Tester Roles: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Software development has become increasingly complex, necessitating specialized roles to enhance product quality and optimize overall software development processes. This report aims to explore the key distinctions between Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET) and Tester roles, shedding light on their unique responsibilities, skillsets, and contributions within the broader software development cycle.
Who is SDET?
Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET) is a master multitasker in the realm of software quality. They are the tech virtuosos, juggling code, testing strategies, and quality assurance with finesse. Software Development Engineers in Test embody the perfect blend of a software developer’s precision and a tester’s discerning eye. As they meticulously code, debug, and craft test cases, they ensure that every line of code dances to the tune of flawlessness. They are the guardians of software integrity, maintaining the delicate balance between functionality and reliability. And if you’re aspiring to ascend to these heights of technical prowess, Wedevx platform stands as a guiding beacon. With their comprehensive Software Development Engineer in Test courses, Wedevx paves the path for anyone eager to become a proficient SDET, providing the essential knowledge and skills needed to excel in this dynamic field.
Check out our blog on “What is SDET?” for a more detailed understanding of who they are and how to possibly become one.
Who is a Tester?
Tester, in the world of software, is akin to a vigilant detective in a constantly evolving mystery novel. They are meticulous examiners, scrutinizing every line of code, every functionality, and every user interface to unveil defects and ensure the software’s quality. Testers possess an innate ability to think like end-users, to predict how they might interact with the software, and to anticipate potential issues. They are the quality custodians, ensuring that the final product meets the promised standards. Armed with a toolkit of testing methodologies and a keen eye for detail, testers perform a critical role in the software development process, striving to deliver a seamless and delightful user experience. Their job is both an art and a science, demanding a fine balance of technical expertise, critical thinking, and creativity. For those who are passionate about the pursuit of excellence in software, the path of a tester is an enthralling journey worth undertaking.
AI POWERED
CODING PLATFORM
- DEVXAI ASSISTANT
- 300+ CODING EXERCISES
- REAL-LIFE CODING EXERCISES
Role Overview
At a high level, both SDET and Tester positions revolve around ensuring software quality through testing, but their specific areas of focus and responsibilities differ significantly. Testers primarily focus on conducting manual or automated tests to identify any defects or bugs within the software, whereas Software Development Engineers in Test typically possess a broader skillset that combines development expertise with testing proficiency.
Skillset Requirements
A primary distinction between Software Development Engineers in Test and Testers lies in their required skillsets. Whereas Testers predominantly concentrate on elaborating test plans, running test cases, and documenting outcomes, SDETs possess a strong coding background and expertise in programming languages, enabling them to develop and implement automated tests and tools.
Scope of Responsibilities
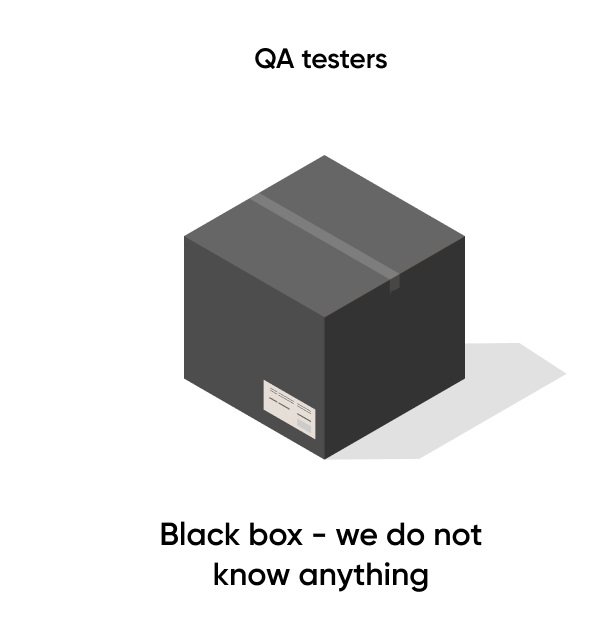
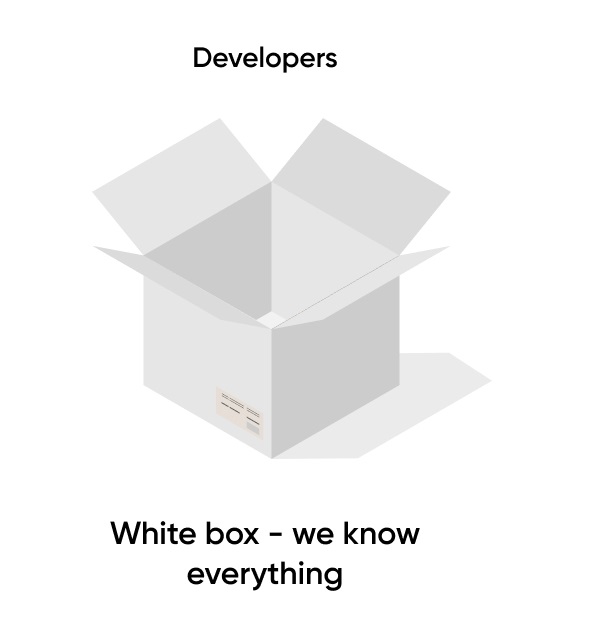
Software Development Engineers in Test undertake a wider array of tasks beyond traditional testing activities. They often collaborate with developers to create testable code, design testing frameworks, and establish effective procedures for test automation. Testers, on the other hand, focus primarily on executing established test cases, assessing their outcomes, and providing input to improve software quality. It’s effectively a comparison between black-and-white box testing.
Software Development Involvement
One of the key differences between SDETs and Testers is their involvement in the software development process. While Testers typically join the process during the testing phase, Software Development Engineers in Test work in conjunction with developers throughout the entire software development lifecycle, ensuring quality assurance measures are implemented at each stage.
Test Automation Expertise
Automation plays a crucial role in modern software development, and Software Development Engineers in Test possess the necessary skills to develop and maintain automated testing frameworks. SDETs harness their strong coding abilities to create robust and scalable test scripts, significantly reducing testing effort and improving overall efficiency. Testers, however, focus more on executing and maintaining these automated tests, without deep involvement in their development.
Technical Proficiency
Given their coding proficiency, Software Development Engineers in Test are often equipped to identify potential software issues at a more granular level. Their advanced technical knowledge allows them to perform white-box testing, examining application structures and code snippets, while Testers primarily rely on black-box testing techniques, focusing on external inputs and expected outputs.
Debugging and Troubleshooting
In terms of debugging and troubleshooting, Software Development Engineers in Test possess an advantage due to their deeper understanding of the software’s inner workings. Their technical expertise enables them to identify the root cause of defects more efficiently, facilitating faster and more targeted problem-solving. Testers, while skilled in identifying issues, may require additional collaboration with developers to uncover the underlying causes.
Collaborative Nature
Collaboration is an essential aspect of both SDET and Tester roles. However, Software Development Engineers in Test typically engage more extensively with various stakeholders, such as developers and product managers. They actively participate in cross-functional teams, offering valuable insights into software quality throughout the development process. Testers often interact more with quality assurance teams, reporting defects, and suggesting improvements.

Continuous Learning
Both SDET and Tester roles require a mindset of continuous learning to adapt to evolving technologies and industry trends. However, given the Software Development Engineers in Test broader skillset, they are often at the forefront of emerging practices, incorporating new tools and methodologies into their testing strategies. Testers, while also developing their proficiency, may have a more specialized focus on the refinement and optimization of established testing practices.
Conclusion
In summary, SDETs and Testers play indispensable roles in software development, each contributing distinctively towards ensuring quality and enhancing end-user satisfaction. The Software Development Engineers in Test coding proficiency, involvement in the entire development lifecycle, and expertise in test automation set them apart from Testers, who primarily focus on executing and refining test cases. By recognizing these key differences, organizations can better leverage both roles simultaneously to achieve unparalleled software quality and excellence.
Aspiring to become a proficient SDET? Embracing the comprehensive SDET courses offered by Wedevx can provide you with the essential knowledge and skills needed to excel in this dynamic and vital role, where technical prowess meets testing expertise.